Late-night snacking or eating a full meal late at night has become a common habit for many people due to busy schedules, irregular work hours, or cravings. While it may seem harmless, this habit can have a profound impact on metabolism and overall health. In this article, we will explore the effects of eating late at night, supported by scientific research, and provide tips to manage nighttime hunger.
Why Do People Eat Late at Night?
Late-night eating often stems from various lifestyle and psychological factors:
- Busy Schedules: Work or social commitments can lead to skipped meals during the day, pushing meals to later hours.
- Stress and Emotional Eating: Stress and anxiety can trigger cravings for comfort foods, often late at night.
- Irregular Sleep Patterns: People who stay up late or suffer from insomnia may feel hungry and indulge in midnight snacks.
- Cultural or Social Habits: In some cultures or households, late dinners are a norm.
Although occasional late-night eating may not seem like a big deal, repeated patterns can significantly affect the body’s functioning.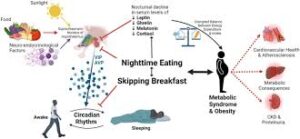
How Eating Late Affects Metabolism
1. Disruption of Circadian Rhythm
The body follows a natural circadian rhythm, a 24-hour biological clock that regulates sleep, digestion, and metabolism. Eating late at night disrupts this rhythm, leading to inefficient digestion and energy usage. Studies show that consuming food outside the body’s optimal eating window can impair glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of metabolic disorders.
2. Weight Gain and Obesity
Eating late is often associated with higher calorie intake, as people tend to choose calorie-dense, less nutritious foods. Additionally, the body’s ability to burn calories slows down at night. This creates an imbalance where more calories are stored as fat, contributing to weight gain and obesity.
3. Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Late-night meals can cause a spike in blood sugar levels, especially if they are high in carbohydrates. Over time, this can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. A study published in Diabetes Care found that nighttime eating can exacerbate glucose intolerance and negatively affect metabolism.
4. Reduced Fat Burning
During sleep, the body shifts into repair and fat-burning mode. Late-night eating interferes with this process, as the body prioritizes digestion over fat breakdown. This can hinder weight management efforts and lead to fat accumulation.
Health Consequences of Late-Night Eating
1. Poor Sleep Quality
Eating close to bedtime can cause discomfort, indigestion, or acid reflux, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. Poor sleep quality further impacts metabolism, leading to hormonal imbalances that increase hunger and cravings the following day.
2. Higher Risk of Heart Disease
Research suggests that eating late at night increases triglyceride levels, which are linked to a higher risk of heart disease. The body’s inability to properly process late-night meals may also elevate cholesterol levels over time.
3. Gastrointestinal Issues
Consuming food right before lying down can lead to acid reflux and heartburn. The horizontal position during sleep allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and potential long-term damage to the esophageal lining.
4. Mental Health Impact
Late-night eating is often accompanied by guilt or stress about weight gain. This cycle can negatively impact mental health, contributing to anxiety, stress, or poor self-esteem.
Tips to Avoid Eating Late at Night
1. Stick to a Regular Eating Schedule
Plan meals and snacks at consistent times during the day to prevent excessive hunger at night. A well-balanced dinner can help curb nighttime cravings.
2. Stay Hydrated
Sometimes, thirst is mistaken for hunger. Drinking a glass of water before reaching for a late-night snack can help determine if you’re truly hungry.
3. Choose Nutrient-Dense Foods
If you must eat at night, opt for small portions of healthy, nutrient-dense foods like yogurt, nuts, or fruits instead of processed or high-sugar snacks.
4. Manage Stress and Emotional Eating
Engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation, exercise, or journaling to avoid emotional eating.
5. Improve Sleep Hygiene
Establish a bedtime routine to promote better sleep and reduce the likelihood of staying awake and feeling hungry late at night.
Eating late at night can significantly affect metabolism, weight, and overall health. It disrupts the body’s natural processes, leading to issues like poor sleep, weight gain, and increased risk of chronic diseases. By understanding these impacts and making conscious choices, you can break the habit of late-night eating and support your overall health.
Discover how eating late at night affects your metabolism, weight, and health. Learn tips to manage late-night cravings and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is eating late at night always bad?
While occasional late-night eating is not harmful, making it a habit can disrupt metabolism, lead to weight gain, and increase the risk of health issues like diabetes and heart disease.
2. What are the best foods to eat late at night?
If you must eat late, opt for light and healthy snacks like Greek yogurt, a handful of nuts, or a piece of fruit. Avoid processed, sugary, or fatty foods.
3. Can late-night eating cause insomnia?
Yes, eating heavy meals close to bedtime can cause discomfort and indigestion, which can interfere with sleep quality.
4. How long before bed should I stop eating?
It’s generally recommended to stop eating 2-3 hours before bedtime to allow proper digestion and promote better sleep.
5. Does eating late affect muscle growth?
Late-night protein snacks may support muscle repair and growth, but overindulging in high-calorie meals can counteract fitness goals by promoting fat gain.
By addressing these common questions and providing actionable advice, you can take control of your eating habits and optimize your health.