Discover how mental health is intricately linked to chronic diseases, and learn why understanding this connection is crucial for better health and well-being.
The Overlooked Link Between Mental Health and Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis, are prevalent worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. These long-term conditions often come with a range of physical symptoms that require management, medications, and lifestyle adjustments. However, what is less commonly discussed is the profound impact these diseases have on mental health.
Research has shown that there is a strong connection between mental health and chronic diseases—one that can significantly affect the quality of life, disease progression, and overall well-being. Understanding this hidden link is crucial not only for better managing chronic diseases but also for addressing the mental health challenges that often accompany them.
In this article, we will explore the complex relationship between mental health and chronic diseases, uncover the ways in which one can affect the other, and provide insights into how managing both can improve the overall quality of life.
Understanding the Connection: How Mental Health Affects Chronic Diseases
The Impact of Chronic Diseases on Mental Health
Chronic diseases often come with a significant emotional toll. Individuals who live with conditions like diabetes, asthma, or chronic pain may experience feelings of frustration, sadness, and even helplessness. The ongoing struggle to manage symptoms, coupled with the uncertainty about disease progression, can contribute to mental health issues, including:
- Depression: Research indicates that individuals with chronic diseases are at a higher risk of developing depression. The constant physical discomfort and lifestyle restrictions imposed by chronic illnesses can lead to feelings of isolation and hopelessness.
- Anxiety: Worry about disease management, future complications, and medical appointments can create a constant sense of anxiety. The fear of disease progression or the unknown can be overwhelming for many individuals.
- Stress: Chronic illness often brings about financial stress due to medical costs, disability, or loss of work. This can result in heightened levels of stress, which can further exacerbate physical symptoms and negatively impact overall health.
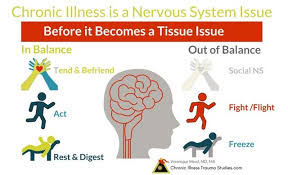
How Chronic Diseases Impact Brain Function
Chronic illnesses can also affect brain function, leading to cognitive challenges, such as memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and mental fatigue. For example:
- Diabetes: Long-term high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and reduce oxygen supply to the brain, leading to cognitive decline. Additionally, diabetes-related stress can contribute to feelings of mental exhaustion.
- Heart Disease: Poor heart health can lead to decreased blood flow to the brain, impairing mental clarity and focus. Furthermore, the emotional burden of managing heart disease can increase the risk of anxiety and depression.
The Role of Inflammation in Both Mental and Physical Health
Chronic diseases often involve inflammation within the body, which has been linked to mental health conditions as well. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and cardiovascular diseases trigger inflammation, which can affect the brain and neurotransmitter function. Studies have shown that elevated levels of inflammatory markers are associated with depression, cognitive dysfunction, and other mental health conditions.
How Mental Health Impacts Chronic Diseases
The Influence of Stress on Disease Progression
Mental health issues, particularly chronic stress, can influence the severity and progression of chronic diseases. Stress activates the body’s “fight or flight” response, which can trigger a cascade of hormonal and physical changes. Over time, chronic stress may:
- Weaken the immune system: Making it harder for the body to fight infections and illnesses.
- Increase inflammation: Further exacerbating conditions like arthritis, heart disease, and asthma.
- Increase unhealthy habits: People dealing with mental health challenges may turn to smoking, unhealthy eating, or sedentary behavior, all of which contribute to the worsening of chronic diseases.
Depression and Disease Management
Depression can create significant barriers to managing chronic diseases effectively. Individuals who are depressed may experience fatigue, lack of motivation, and a diminished sense of self-worth. These factors can make it difficult to adhere to treatment plans, take medications as prescribed, or maintain healthy lifestyle habits.
For example, people with depression may struggle to exercise regularly or eat a balanced diet, both of which are essential for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. As a result, disease progression may accelerate, leading to worse health outcomes.
Anxiety and Health Behaviors
Anxiety also has a profound impact on managing chronic diseases. People with anxiety disorders often experience heightened levels of fear about their health, leading them to avoid necessary medical appointments or treatment. In some cases, this avoidance can delay diagnosis or treatment, causing chronic conditions to worsen. Furthermore, anxiety can lead to poor sleep, which negatively impacts both mental and physical health.
Managing Both Mental Health and Chronic Diseases: The Path to Better Health
The Importance of Integrated Care
Given the strong link between mental health and chronic diseases, integrated care approaches are essential. This means treating both the physical and mental health aspects of chronic disease simultaneously. Integrated care might include:
- Mental health counseling: Addressing mental health concerns through therapy or counseling can help individuals develop coping strategies, improve their outlook, and reduce stress.
- Medication management: Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, or other mental health treatments can be prescribed alongside medications for chronic diseases.
- Lifestyle changes: Encouraging exercise, proper nutrition, and relaxation techniques can improve both mental and physical health.
By adopting a holistic approach, patients can better manage both their chronic conditions and mental health, leading to improved overall outcomes.
The Role of Support Networks
Support networks are also critical in managing both mental health and chronic diseases. Family members, friends, or support groups can provide emotional support, encouragement, and practical help, which can make a significant difference in a patient’s well-being. Being part of a community of individuals who understand the challenges of living with chronic disease can help reduce feelings of isolation and improve mental health.
Healthy Lifestyle Changes for Improved Mental and Physical Health
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can be one of the most effective ways to manage both mental health and chronic disease. Some key strategies include:
- Regular physical activity: Exercise has been shown to improve both mood and physical health. Even moderate activity can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety while improving chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
- Balanced nutrition: Eating a healthy, balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support both mental health and disease management. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins are particularly beneficial for brain health.
- Mindfulness and relaxation: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress, reduce anxiety, and promote a sense of well-being.
Conclusion: Breaking the Cycle for Better Health and Well-Being
The hidden connection between mental health and chronic diseases is clear: each can exacerbate the other, creating a cycle of physical and emotional distress. However, by recognizing this connection and adopting an integrated approach to care, individuals can improve both their mental health and chronic disease outcomes.
With the right combination of therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and support, people living with chronic diseases can manage their physical health while also caring for their emotional well-being. It is time to break the cycle and take a more holistic approach to health—one that addresses both the body and the mind.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about Mental Health and Chronic Diseases
Q1: Can chronic diseases cause mental health issues? Yes, chronic diseases can increase the risk of mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, and stress due to the ongoing physical burden and lifestyle changes they cause.
Q2: How does mental health affect chronic disease management? Poor mental health can lead to difficulties in managing chronic diseases, as depression, anxiety, and stress can reduce motivation, disrupt routines, and interfere with following treatment plans.
Q3: What are some strategies for managing both mental health and chronic diseases? Effective strategies include integrated care approaches, therapy or counseling, medication management, regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and building strong support networks.
Q4: How can inflammation from chronic diseases affect mental health? Chronic diseases that involve inflammation, such as heart disease or arthritis, can increase inflammation in the brain, potentially leading to symptoms of depression or cognitive decline.
Q5: Can exercise improve both mental and physical health? Yes, regular physical activity has been shown to improve mood, reduce anxiety, and help manage chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis.