Discover how micronutrients play a crucial role in boosting immune function. Learn about essential vitamins and minerals that strengthen immunity and promote better health.
In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining a healthy immune system is more important than ever. While regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management are well-known practices for boosting immunity, one often overlooked yet powerful way to enhance immune function is through the consumption of micronutrients. These vital nutrients, although required by the body in small amounts, have a significant impact on the immune system’s ability to ward off infections and diseases.
This article explores the essential role of micronutrients in immune health, focusing on vitamins and minerals that contribute to a robust immune system. We’ll break down how each micronutrient supports immune function, why they are vital, and how to ensure you’re getting enough through diet and supplementation.
What Are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals that the body needs in small amounts but are critical for maintaining optimal health. Unlike macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) that provide energy, micronutrients support a variety of functions in the body, including immune function, cellular repair, and metabolism regulation.
While the body needs micronutrients in relatively small quantities, deficiencies can lead to weakened immunity, making you more susceptible to infections and diseases. Ensuring adequate intake of these nutrients is key to a functioning immune system.
Types of Micronutrients Essential for Immunity
- Vitamins
Vitamins are organic compounds that are crucial for the body’s various metabolic processes, including immune response. Key immune-boosting vitamins include Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin A, and the B vitamins. - Minerals
Minerals are inorganic elements that contribute to a wide range of biological processes. Minerals like zinc, iron, and selenium are particularly important for immune function.
Key Micronutrients for Immune Health
1. Vitamin C: The Immune Powerhouse
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is perhaps the most famous immune-boosting micronutrient. This water-soluble vitamin is a potent antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative stress and supports the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. Vitamin C also enhances the function of the skin’s barrier, which acts as the body’s first line of defense against pathogens.
Benefits of Vitamin C for Immunity:
- Stimulates the production and function of white blood cells
- Acts as a powerful antioxidant to protect cells from damage
- Enhances skin barrier function to protect against pathogens
Sources of Vitamin C: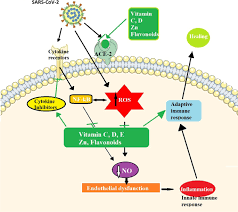
- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits)
- Berries (strawberries, raspberries, blueberries)
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Kale and spinach
2. Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
Vitamin D plays a pivotal role in regulating immune responses and reducing inflammation. It enhances the pathogen-fighting effects of monocytes and macrophages, which are types of white blood cells that help in defending against infections. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to increased susceptibility to autoimmune diseases and respiratory infections.
Benefits of Vitamin D for Immunity:
- Strengthens the pathogen-fighting effects of immune cells
- Regulates inflammation and reduces the risk of autoimmune diseases
- Supports the body’s defense against respiratory infections
Sources of Vitamin D:
- Sunlight exposure (the body produces Vitamin D when the skin is exposed to sunlight)
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Fortified foods (milk, cereals, and orange juice)
- Egg yolks
3. Vitamin A: The Visionary Immune Boost
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy mucosal surfaces (such as in the lungs and digestive system), which are key barriers to infection. It supports the immune system by regulating the growth and differentiation of immune cells, such as T-cells. Moreover, Vitamin A is vital for the functioning of the skin, which acts as an additional defense line against harmful pathogens.
Benefits of Vitamin A for Immunity:
- Supports mucosal immunity in the respiratory and digestive systems
- Enhances the function of T-cells, which are crucial for immune responses
- Contributes to skin health and overall barrier protection
Sources of Vitamin A:
- Carrots
- Sweet potatoes
- Spinach and kale
- Liver
- Red bell peppers
4. Zinc: The Immune System Ally
Zinc is a trace mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining immune cell function. It is involved in the development and activation of T-cells, which are vital for defending the body against pathogens. Zinc also supports the integrity of the skin, acting as a barrier to pathogens, and has anti-inflammatory properties that help manage immune responses.
Benefits of Zinc for Immunity:
- Enhances the production and function of T-cells
- Regulates the immune response and reduces inflammation
- Strengthens skin health and wound healing
Sources of Zinc:
- Oysters and other shellfish
- Meat (beef, pork, and chicken)
- Legumes (chickpeas, lentils)
- Seeds (pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds)
- Nuts (cashews, almonds)
5. Iron: The Oxygen Carrier for Immune Cells
Iron is an essential mineral that supports the production of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood. Adequate oxygen levels are crucial for the optimal function of immune cells. Iron also plays a significant role in the production of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell involved in immune responses.
Benefits of Iron for Immunity:
- Supports oxygen transport to immune cells
- Essential for the production of lymphocytes
- Helps prevent iron-deficiency anemia, which can weaken the immune system
Sources of Iron:
- Red meat (beef, lamb)
- Poultry (chicken, turkey)
- Legumes (lentils, beans)
- Tofu and fortified cereals
6. Selenium: The Antioxidant Mineral
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that works as an antioxidant, helping protect cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. It plays an important role in the immune system by promoting the production of certain immune cells and enhancing the body’s defense mechanisms against viral infections.
Benefits of Selenium for Immunity:
- Acts as a potent antioxidant to protect cells from damage
- Enhances immune cell function and viral defense
- Supports thyroid health, which is vital for overall metabolic function
Sources of Selenium:
- Brazil nuts (one of the best sources)
- Seafood (tuna, shrimp, and oysters)
- Whole grains
- Eggs
How to Ensure Adequate Micronutrient Intake for Immune Support
A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is the best way to ensure that you are getting the necessary micronutrients for a strong immune system. However, many people struggle to meet their daily micronutrient needs through diet alone. In such cases, dietary supplements may be a helpful addition, though it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation regimen.
Tips for Boosting Micronutrient Intake:
- Include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your diet to ensure a range of vitamins and minerals.
- Opt for whole foods rather than processed foods to maximize nutrient density.
- Consider consulting with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized nutrition plan that meets your immune-boosting needs.
Micronutrients play a critical role in supporting immune function and protecting the body against harmful pathogens. From Vitamin C’s powerful antioxidant properties to zinc’s role in enhancing immune cell activity, each micronutrient contributes uniquely to immune health. By consuming a well-rounded diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals, you can help ensure that your immune system is strong and ready to fight off infections.
Remember, a balanced diet is the foundation of health, and while supplements can help fill gaps in your nutrition, they should not replace a healthy lifestyle. By prioritizing micronutrients, you are investing in long-term immune health and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are micronutrients?
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals that are needed in small amounts by the body. Despite being required in tiny quantities, they play an essential role in maintaining optimal health, including supporting immune function.
2. How do micronutrients boost immune function?
Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, help regulate the immune response, support the production of immune cells, and protect cells from oxidative stress. They are crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system.
3. What are the best sources of Vitamin C?
Vitamin C can be found in citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), berries, bell peppers, broccoli, and spinach. Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables can help ensure you get enough Vitamin C to boost immunity.
4. Can a deficiency in micronutrients affect my immune system?
Yes, deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections. It is important to consume adequate amounts of micronutrients through diet or supplements.
5. Are there any risks to taking too many micronutrients?
Yes, taking excessive amounts of certain micronutrients, especially through supplements, can lead to toxicity and harmful side effects. It’s important to follow recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider before taking supplements.
6. Can supplements replace a healthy diet?
While supplements can help fill nutritional gaps, they cannot replace a balanced diet rich in whole foods. It is always best to aim for a nutrient-dense diet to support overall health and immune function.