In the realm of nutrition, micronutrients often take a backseat to their macronutrient counterparts. However, these essential vitamins and minerals play a critical role in sustaining life, promoting growth, and supporting healing processes. From boosting energy levels to enhancing immune function, micronutrients are indispensable for maintaining overall health. In this article, we delve deep into what micronutrients are, why they are crucial, and how to ensure you’re getting enough of them.
What Are Micronutrients?
Definition and Classification
Micronutrients are nutrients required by the body in small amounts but are crucial for vital physiological functions. They are broadly classified into two categories:
- Vitamins: Organic compounds that support various biochemical processes. Examples include Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and B-complex vitamins.
- Minerals: Inorganic substances essential for body structure and function. Examples include calcium, iron, and zinc.
The Role of Micronutrients in the Body
Micronutrients contribute to: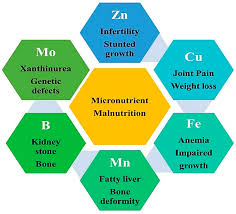
- Energy production: B-vitamins like B6, B12, and niacin are involved in metabolic pathways that generate energy.
- Growth and development: Vitamin D and calcium are essential for bone development.
- Wound healing and immunity: Zinc and Vitamin C accelerate healing and enhance immune responses.
Importance of Micronutrients for Health
1. Energy
Micronutrients such as magnesium and B-vitamins play a pivotal role in converting food into energy. Without adequate levels, individuals may experience fatigue and diminished performance.
2. Growth
Micronutrients like iodine and iron are essential during periods of rapid growth, such as childhood and adolescence. Deficiencies can lead to developmental delays and growth issues.
3. Healing
Vitamins A and C, along with zinc, support the body’s natural repair processes, aiding in faster recovery from injuries and surgeries.
Common Micronutrient Deficiencies
Despite their importance, micronutrient deficiencies remain a global concern. Here are some common deficiencies:
Iron Deficiency
- Impact: Leads to anemia, characterized by fatigue and decreased immunity.
- Sources: Red meat, lentils, spinach.
Vitamin D Deficiency
- Impact: Results in weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
- Sources: Sunlight, fatty fish, fortified dairy products.
Iodine Deficiency
- Impact: Causes goiter and developmental issues in children.
- Sources: Iodized salt, seafood, dairy products.
How to Ensure Adequate Micronutrient Intake
Balanced Diet
A diverse diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy can provide most micronutrients naturally.
Fortified Foods
Foods fortified with vitamins and minerals, such as fortified cereals and milk, can help bridge dietary gaps.
Supplements
For individuals unable to meet their needs through diet alone, supplements may be necessary. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
Top Micronutrient-Rich Foods
- Vitamin A: Sweet potatoes, carrots, and spinach.
- Vitamin C: Oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers.
- Iron: Red meat, tofu, and legumes.
- Calcium: Milk, yogurt, and cheese.
- Zinc: Shellfish, nuts, and seeds.
The Risks of Overconsumption
While deficiencies can harm health, excessive intake of certain micronutrients, such as Vitamin A and iron, can lead to toxicity. Symptoms may include nausea, liver damage, and even long-term health complications. Moderation is key.
Micronutrients and Chronic Disease Prevention
1. Cardiovascular Health
- Role: Magnesium and potassium help regulate blood pressure and prevent heart disease.
- Sources: Leafy greens, bananas, and nuts.
2. Bone Health
- Role: Calcium and Vitamin D prevent osteoporosis and maintain bone density.
- Sources: Dairy products, fortified plant-based milks, and sunlight exposure.
3. Immune Support
- Role: Zinc and Vitamin C boost immune defenses and reduce the severity of infections.
- Sources: Citrus fruits, shellfish, and fortified cereals.
“Discover the essential role of micronutrients in energy, growth, and healing. Learn about key vitamins and minerals, common deficiencies, and tips to ensure optimal health.”
Conclusion
Micronutrients are the unsung heroes of our diets. Despite their small quantities, their impact on energy, growth, and healing is profound. By adopting a balanced diet rich in diverse food groups, you can ensure adequate micronutrient intake and pave the way for optimal health.
FAQ
1. What are micronutrients, and why are they important?
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals essential for energy production, growth, and healing. They support vital bodily functions and prevent chronic diseases.
2. What are the symptoms of micronutrient deficiencies?
Common symptoms include fatigue, weakened immunity, developmental delays, and bone weakness, depending on the specific deficiency.
3. Can I get all the micronutrients from diet alone?
Yes, a well-balanced diet can provide most micronutrients. However, supplements may be needed for those with specific deficiencies or dietary restrictions.
4. What are the risks of taking too many micronutrients?
Overconsumption of certain micronutrients, such as Vitamin A or iron, can lead to toxicity and adverse health effects. Always follow recommended guidelines.
5. How do micronutrients differ from macronutrients?
Micronutrients are needed in smaller quantities compared to macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, but they are equally vital for overall health.
By prioritizing micronutrient-rich foods and maintaining awareness of potential deficiencies, you can harness the power of these essential components to fuel energy, foster growth, and enhance healing. Take charge of your nutrition today!