Social health is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of overall well-being. While physical and mental health receive much attention, social health—the ability to form and maintain meaningful relationships and support systems—is equally vital. Strong social health can enhance life satisfaction, improve mental health, and even boost physical health. This article explores the concept of social health, its importance, and actionable steps to build robust relationships and support systems.
What is Social Health?
Social health refers to the quality of relationships you have with others, your ability to maintain meaningful connections, and the support systems you can rely on during challenging times. It involves effective communication, empathy, trust, and mutual respect in your interactions.
Key Components of Social Health
- Strong Interpersonal Relationships
- These include connections with family, friends, colleagues, and romantic partners.
- Effective Communication Skills
- Active listening, clear articulation, and understanding non-verbal cues.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Recognizing, understanding, and managing your emotions and those of others.
- Conflict Resolution Skills
- Addressing disagreements constructively to strengthen relationships
- Addressing disagreements constructively to strengthen relationships
The Importance of Social Health
Enhances Mental Well-Being
Strong social connections reduce the risk of depression, anxiety, and loneliness. Supportive relationships provide emotional comfort and foster a sense of belonging.
Boosts Physical Health
Studies show that social isolation can lead to increased risks of heart disease, high blood pressure, and weakened immunity. In contrast, supportive relationships promote better health outcomes.
Builds Resilience
Having a solid support system helps you navigate life’s challenges. Whether facing a personal crisis or workplace stress, knowing you have people to rely on fosters resilience.
Promotes Personal Growth
Interacting with diverse individuals exposes you to new ideas, perspectives, and experiences, contributing to personal and intellectual growth.
How to Build Strong Relationships
1. Prioritize Quality Time
Spending meaningful time with loved ones strengthens bonds. This could involve regular family dinners, weekend outings, or simply checking in through phone calls or texts.
2. Practice Active Listening
Listen to understand, not just to respond. Show genuine interest in what others have to say and validate their feelings.
3. Show Appreciation
Express gratitude and appreciation for the people in your life. A simple “thank you” or compliment can go a long way.
4. Be Empathetic
Try to understand others’ perspectives and feelings. Empathy builds trust and strengthens connections.
5. Resolve Conflicts Constructively
Instead of avoiding conflicts, address them calmly and respectfully. Focus on finding solutions rather than assigning blame.
6. Set Healthy Boundaries
Boundaries protect your time, energy, and emotional well-being. Communicate your limits clearly to others.
Creating Support Systems
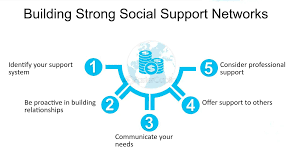
Identify Your Support Network
Your support network can include family, friends, mentors, colleagues, or even support groups. Identify the people you trust and who have positively influenced your life.
Invest in Reciprocal Relationships
Healthy support systems thrive on mutual give-and-take. Be there for others just as you’d expect them to be there for you.
Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, professional guidance from counselors or therapists can be invaluable, especially when dealing with complex personal issues.
Join Community Groups
Participating in clubs, volunteer organizations, or hobby groups can expand your support network and introduce you to like-minded individuals.
Overcoming Challenges in Social Health
1. Dealing with Loneliness
- Recognize loneliness as a signal to reconnect with others or build new relationships.
- Join community events, take up a hobby, or volunteer.
2. Managing Social Anxiety
- Start small by interacting with people in low-pressure settings.
- Practice relaxation techniques and seek therapy if needed.
3. Rebuilding Broken Relationships
- Apologize sincerely for past mistakes.
- Show consistent effort to regain trust and improve communication.
Conclusion
Social health is a cornerstone of a fulfilling life. Building strong relationships and support systems enhances mental and physical well-being, provides emotional resilience, and fosters personal growth. By prioritizing meaningful connections, practicing empathy, and cultivating effective communication, you can significantly improve your social health. Remember, nurturing your relationships is an ongoing process that requires time, effort, and a genuine desire to connect.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are examples of good social health?
Examples include having a strong support network, resolving conflicts constructively, and maintaining meaningful connections with friends and family.
2. How does social health affect mental health?
Good social health reduces feelings of loneliness and stress, providing emotional support that enhances mental well-being.
3. Can social health improve physical health?
Yes, strong social connections are linked to better cardiovascular health, a robust immune system, and overall longevity.
4. How can I improve my social health?
You can improve social health by spending quality time with loved ones, practicing active listening, showing appreciation, and joining community groups.
5. What is the role of technology in social health?
Technology can enhance social health by enabling connections across distances. However, it’s essential to balance online interactions with face-to-face relationships for a well-rounded social experience.