Discover how micronutrients—small yet powerful nutrients—impact your health. Learn why they are essential for optimal wellness and how to incorporate them into your diet.
Understanding the Power of Micronutrients
When we think about maintaining good health, we often focus on macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. However, there’s a group of nutrients that, despite being required in smaller amounts, play an equally crucial role in our overall well-being: micronutrients. These include vitamins and minerals, which are often overlooked yet are vital for a wide range of bodily functions.
In this article, we explore the incredible power of micronutrients, how they influence various bodily systems, and how you can ensure you’re getting enough of them in your diet. Whether you’re aiming for better energy, immunity, or mental health, understanding the role of micronutrients is key.
What Are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are nutrients that are required by the body in relatively small amounts. These include vitamins, minerals, and trace elements, all of which are essential for various physiological processes. Despite their small quantity, micronutrients have a significant impact on our health, from maintaining a strong immune system to supporting brain function and promoting overall vitality.
Types of Micronutrients
- Vitamins: These organic compounds are essential for various metabolic processes. They help our bodies convert food into energy, build strong bones, and protect against disease. Some well-known vitamins include:
- Vitamin A (for eye health)
- Vitamin C (for immune support)
- Vitamin D (for bone health)
- Vitamin E (for skin health)
- Minerals: These inorganic elements are involved in processes like bone formation, fluid balance, and nerve function. Key minerals include:
- Calcium (for bones and teeth)
- Iron (for blood oxygen transport)
- Magnesium (for muscle and nerve function)
- Potassium (for heart function)
- Trace Elements: These are needed in very small amounts but are still critical to health. Examples include:
- Zinc (for immune function)
- Iodine (for thyroid health)
- Selenium (for antioxidant protection)
Why Micronutrients Are Essential for Your Health
1. Support for Immune Function
Micronutrients are integral to maintaining a healthy immune system. Vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, and selenium help strengthen the body’s defenses against infections. A deficiency in these micronutrients can leave the immune system vulnerable, making it harder to fight off viruses and bacteria.
- Vitamin C is known for its role in boosting the production of white blood cells, which are critical for fighting infections.
- Vitamin D enhances pathogen-fighting effects in immune cells, making it essential during flu season.
2. Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Your brain relies on micronutrients to function properly. Deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals can negatively impact memory, concentration, and mood. For instance:
- B Vitamins, especially B6, B12, and folate, are crucial for brain health. These vitamins help in the production of neurotransmitters, chemicals that transmit messages between nerve cells.
- Magnesium is involved in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body, many of which affect nerve function and cognitive processes. Low levels of magnesium are associated with an increased risk of depression and cognitive decline.
3. Energy Production
While macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats provide the bulk of energy required by the body, micronutrients play an essential supporting role in energy production. Many micronutrients, especially B vitamins, help the body convert food into energy efficiently. Without an adequate intake of vitamins like B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), and B3 (niacin), energy production can be impaired, leading to fatigue and lethargy.
4. Bone Health
Micronutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium are crucial for maintaining strong bones and preventing conditions like osteoporosis. Calcium helps build and maintain bone structure, while vitamin D enhances calcium absorption. Magnesium plays a supporting role by contributing to bone density and preventing bone loss.
5. Antioxidant Protection
Some micronutrients, particularly vitamin E, vitamin C, and selenium, act as antioxidants. These protect the body’s cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Oxidative stress is linked to aging, chronic diseases, and inflammation, making antioxidants vital for maintaining health over the long term.
Micronutrient Deficiency: A Growing Concern
Despite their importance, micronutrient deficiencies are common worldwide, often due to poor dietary choices, soil depletion, or underlying health conditions. Inadequate intake of key vitamins and minerals can lead to a range of health issues, such as:
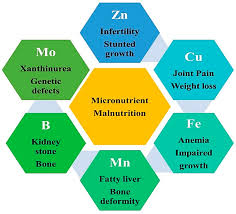
- Iron deficiency: This can lead to anemia, fatigue, and poor immune function.
- Vitamin D deficiency: Often results in weakened bones and a higher susceptibility to infections.
- Iodine deficiency: Can cause thyroid problems, leading to weight gain, fatigue, and cognitive issues.
Ensuring that you’re getting enough micronutrients is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing these issues.
How to Incorporate Micronutrients into Your Diet
The best way to ensure you’re meeting your micronutrient needs is by consuming a balanced, nutrient-dense diet. Here are some practical tips for boosting your intake of vitamins and minerals:
- Eat a Variety of Fruits and Vegetables: Different fruits and vegetables are rich in different micronutrients. For example, leafy greens like spinach are high in magnesium and vitamin K, while citrus fruits are packed with vitamin C.
- Choose Whole Grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats are rich in B vitamins and minerals such as magnesium and iron.
- Include Lean Proteins: Foods like poultry, fish, eggs, and legumes provide key micronutrients like zinc, iron, and vitamin B12.
- Incorporate Dairy and Fortified Foods: Dairy products like yogurt and milk are good sources of calcium and vitamin D. Additionally, some foods like cereals and plant-based milks are fortified with essential micronutrients.
- Consider Supplements: In cases of severe deficiencies or specific health needs, micronutrient supplements may be necessary. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting a supplement regimen.
Micronutrients Are Key to Optimal Health
Micronutrients may only be required in small amounts, but their influence on our health is monumental. From supporting our immune system to enhancing cognitive function and protecting against disease, these small but mighty nutrients are essential for our well-being. By understanding the importance of micronutrients and incorporating them into a balanced diet, we can unlock the full potential of our health.
Remember, achieving optimal health isn’t just about eating the right macronutrients—it’s about ensuring you’re giving your body the vitamins and minerals it needs to thrive.
FAQ: The Power of Micronutrients
Q1: What are the most important micronutrients for overall health?
A1: Some of the most essential micronutrients include vitamin C, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium, and iron. These support immune function, bone health, energy production, and more.
Q2: How can I tell if I have a micronutrient deficiency?
A2: Symptoms of deficiency may include fatigue, weakened immune function, hair loss, and brittle bones. If you’re concerned, it’s important to get a blood test or consult with a healthcare provider.
Q3: Can I get enough micronutrients from a vegan diet?
A3: Yes, a well-planned vegan diet can provide all the necessary micronutrients, though certain nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids may require careful attention or supplementation.
Q4: Are micronutrient supplements necessary?
A4: While it’s best to get micronutrients from food, supplements may be necessary in certain cases, such as when dietary intake is insufficient or in individuals with specific health conditions. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements.
Q5: How can I improve my diet to get more micronutrients?
A5: Focus on eating a wide variety of colorful fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Diversifying your food choices is the best way to ensure you’re getting a broad range of micronutrients.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to the power of micronutrients and their profound effect on our health. Understanding and incorporating these essential nutrients into your diet will help you live a healthier, more vibrant life.